Explained in 60 Seconds: UX & UI
While UX (User Experience) and UI (User Interface) design are both crucial components of delivering an exceptional web experience to end users, they are not the same. We’ll quickly break down the key differences between the two and talk about how the two integrate with each other.
In the wild world of web design, terms like UX and UI get thrown around all the time. But what do these mean exactly? While UX (User Experience) and UI (User Interface) design are both crucial components of delivering an exceptional web experience to end users, they are not the same. We’ll quickly break down the key differences between the two and talk about how the two integrate with each other.
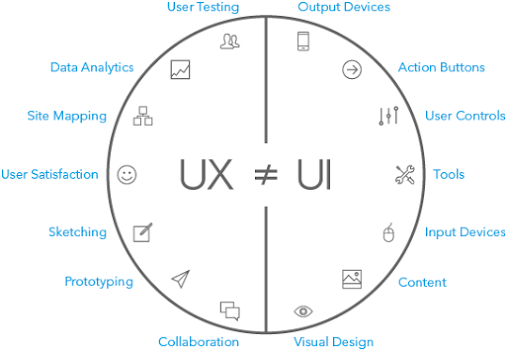
UI primarily encompasses the visual aspects of web design. It develops different layers of presentation and interactivity, giving a product an overall look and feel. Usability.gov, an important resource for web best practices and guidelines, categorizes the different UI elements as:
-
Input - Text field forms, date field forms, dropdown lists, checkboxes, list boxes, clickable buttons, etc.
-
Navigation - Sliders, search field forms, pagination, sidebars, tags, icons, etc.
-
Sharing - Friend lists, follow buttons, like/promote, share buttons, invite friends, etc.
-
Information - Text content, tooltips, message boxes, notifications, icons, progress bar, etc.
User interface design does not just cover what you see when you first come to a page, but also includes the design of what these elements do when a user interacts with them. The weather app below is a prime example of the interactivity component of user interface design being played out:

If UI covers these elements, what is left for UX? User experience design is defined as the process of enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty by improving the usability, ease of use, and pleasure provided in the interaction between the customer and the product. In order to create this high-quality experience between a company and user, user experience designers focus on the processes of research, usability testing, and other aspects of understanding the customer. For example, many UX researchers use A/B testing in order to figure out which of two designs resonates better with an end user.

So, how are these two related exactly? Effective UI and UX design work interchangeably with each other to create an overall pleasing experience for users. If one of them is not up to par, it will significantly affect the performance of a website. For example, a website will feel off if it has great UI and poor UX because it would look amazing but would be terribly difficult to navigate. On the other hand, something that is very usable that looks poor is exemplary of great UX and poor UI.